Greek culture
Temple Architecture
Please click on the image on the right.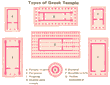
- The simplest form of greek temple is the Temple in antis (A), in which the naos (cella) is preceded by a pronaos (antechamber) flanked by forward projections (antea) of its side walls. There are also examples of a Double anta temple (D), with antea at each side.
- Where there is row of columns in front of the antea (one column in front of each of the antea, with two or four columns in between) the temple is known as Prostyle (C).
- If there is a similar row of columns on the rear end of the temple it is known as Amphiprostyle (F).
- From the second half of the 7th century BCE the classical form was the Peripteral (B) temple, in which the cella was surrounded on all four sides by a colonnade (peristasis) (Parthenon, Athens).
- The Dipteral temple (E) has a double row of columns on all four sites (Temple of Artemis).
- A further type of temple is the Tholos (G), on a circular ground-plan (Epidauros, Delphi).
Classical Orders
Please click on the image on the right.
- In the Doric order the shaft of the column, which tapers towards the top and has between 16 and 20 flutings, stands directly, without a base, on the Stylobate above the three-stepped substructure (Crepidoma). The capital consists of the Echinus and the square Abacus and carries the Architrave with its Frieze of triglyps and metopes.
- The Ionic order has slenderer and gentler forms than the Doric, the 'male' order. The flutings of the columns are separated by narrow ridges. The column stands on a base (for example the Attic type base). The capital has typical spiral volutes on either side. The architrave is made up of three flate sections, each projecting over the one below. The frieze is continuous, without triglyphs to divide it up. This order originates from the Ionian Greek territories.
- The Corinthian order is similar to the Ionic except in the form of the capital. Its characteristic feature is the acanthus leaves which enclose the circular body of the capital, with tendrils reaching up to the corners of the concave architrave. This order was much favoured under the Roman Empire.